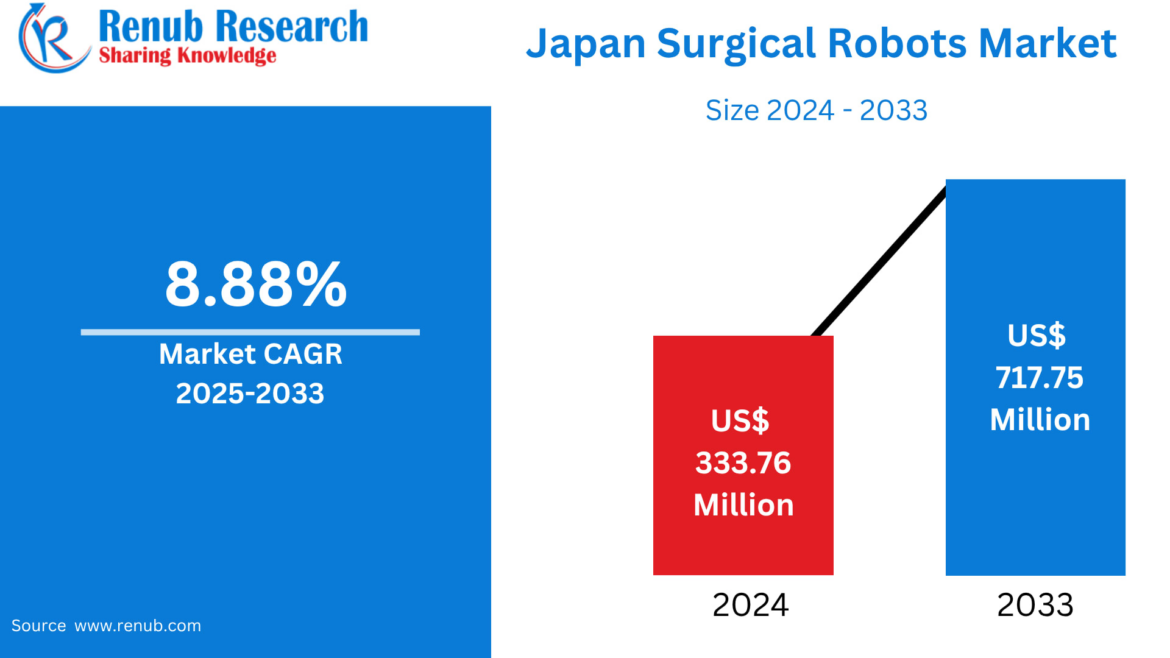
The Japan Surgical Robots Market is entering a new era of rapid transformation, supported by technological breakthroughs, government momentum, and a sharply aging population that increasingly depends on advanced medical interventions. According to Renub Research, the market is projected to grow from US$ 333.76 million in 2024 to US$ 717.75 million by 2033, expanding at a robust CAGR of 8.88% between 2025 and 2033. The rising preference for minimally invasive (MI) surgeries, coupled with Japan’s strategic focus on medical robotics, is turbocharging demand across hospitals nationwide.
As Japan repositions itself as a global leader in next-generation healthcare technology, surgical robots are rapidly becoming the backbone of precision surgery in fields such as orthopedics, neurosurgery, urology, gynecology, and cardiology. From Tokyo’s high-tech medical hubs to emerging centers across Kansai, Aichi, and Kyushu, robotic systems are rewriting the rules of patient care—delivering shorter recovery times, fewer complications, and unrivaled procedural accuracy.
Download Sample Report
Japan Surgical Robots Industry Overview
Surgical robots are computer-guided systems engineered to assist surgeons in performing highly precise minimally invasive procedures. Using tiny instruments mounted on robotic arms and guided by high-definition 3D imaging, these systems allow surgeons to operate with increased dexterity, stability, and visualization.
Equipped with tools such as motion sensors, robotic catheters, advanced optical systems, and data recorders, these robots replicate the delicate hand movements of surgeons—but with greater precision and stability. This makes them especially valuable for operations requiring extreme accuracy, such as neurosurgery, deep-tissue procedures, and microsurgery.
In Japan, demand for robotic-assisted surgeries is rising due to:
High neurological disease prevalence
A rapidly aging population
Strong government funding for medical technology
Growing trust among patients seeking MI surgical options
Hospitals’ push for faster recovery and reduced complications
Neurosurgical robots, in particular, are gaining popularity, helping surgeons navigate deep brain lesions, preserve neuronal structures, and minimize tissue damage—significantly improving patient outcomes.
At the same time, the integration of AI, IoT, VR/AR, and real-time data analytics is amplifying what surgical robots can do. Complex procedures that were once limited to a few specialized centers are gradually becoming mainstream in Japan’s evolving digital healthcare ecosystem.
Key Factors Driving Japan’s Surgical Robots Market Growth
1. An Aging Population Demanding More Surgeries
Japan is home to one of the world’s largest elderly populations, with nearly one-third of citizens aged 65 and above. This demographic shift is directly increasing the demand for surgeries, especially for conditions linked to aging:
Osteoporosis & joint degeneration (orthopedics)
Cardiovascular disorders
Prostate enlargement & urinary tract issues (urology)
Cancer surgeries
Neurological decline
Elderly patients often face higher risks from conventional surgery due to blood loss, trauma, longer healing times, and infection rates. Robotic surgery—being minimally invasive, controlled, and highly precise—significantly reduces these risks.
The result? Hospitals are increasingly adopting robotic systems as the preferred option for elderly patient care.
Robotic surgery helps older adults experience:
Shorter hospital stays
Faster procedure times
Reduced scarring and postoperative pain
Lower complication rates
As Japan’s aging continues to accelerate, robotic-assisted surgery will become indispensable across healthcare institutions.
2. Breakthroughs in Medical Robotics and Imaging
Technological advancements are dramatically reshaping Japan’s surgical capabilities. Newer robotics systems offer:
High-definition, real-time 3D imaging
Greater instrument dexterity and joint articulation
AI-driven decision support
Automated motion stabilization
Surgical navigation and mapping tools
These improvements not only reduce surgical errors but also enable complex procedures to be performed through tiny incisions.
Additionally, machine learning algorithms now help surgical robots:
Predict tissue behavior
Analyze surgical risks
Enhance preoperative planning
Support intraoperative adjustments
Such enhancements significantly improve patient outcomes while reducing recovery time—making robotic systems attractive for both surgeons and hospitals.
3. Government Support and Funding Initiatives
Japan’s government plays a pivotal strategic role in accelerating the adoption of surgical robots. Through policies such as the Future Medical Technology Strategy, the nation is doubling down on robotics, automation, and AI to modernize hospitals and develop more homegrown robotic systems.
Key government initiatives include:
Grants and subsidies for robotic system adoption
Incentives for R&D in medical robotics
Training programs to develop surgeon proficiency
Programs to expand robotic surgery access beyond major urban centers
Support for public–private partnerships in robotics innovation
Japan’s proactive stance is not only supporting the healthcare industry but also positioning the country as a global exporter and technological leader in surgical robotics.
Challenges Slowing Market Expansion in Japan
While Japan’s surgical robotics outlook is highly promising, some challenges remain.
1. High Costs and Affordability Gaps
Surgical robots represent a major financial burden for smaller and rural hospitals. Costs include:
Initial system purchase
Infrastructure upgrades
Annual maintenance contracts
Consumables and accessories
Ongoing software and hardware updates
Surgeon and staff training
While large urban hospitals can absorb these investments, many regional institutions struggle to justify the expenditure—leading to disparities in access to advanced procedures.
2. Limited Training and Surgeon Familiarity
Although robotic surgery demand is rising, many surgeons still have limited exposure to these systems. Barriers include:
Insufficient hands-on training
Heavy workloads hindering skill development
Limited simulation or mentoring programs
Hesitancy in transitioning from traditional surgery
Expanding collaborations between manufacturers, academic institutions, and hospitals is critical to building a strong talent pipeline capable of fully utilizing these technologies.
Japan Surgical Robots Market: Regional Breakdown
Japan’s surgical robot adoption varies significantly across regions. Urban hospitals lead adoption due to better funding, higher patient volumes, and early access to advanced systems.
Below is a regional snapshot:
Tokyo: The Epicenter of Robotic Surgery
Tokyo remains Japan’s strongest and fastest-growing market for surgical robotics. As the nation’s primary medical cluster, Tokyo has:
A dense network of advanced hospitals
Access to government-funded pilot programs
Strong medical research institutions
High patient demand for MI surgeries
More robust surgeon training ecosystems
Tokyo’s leadership role makes it the trendsetter for nationwide adoption.
Kansai: Home to Japan’s First Domestic Surgical Robot
The Kansai region (Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe) is another crucial hub. It is known for:
World-class medical universities
High-tech surgical facilities
Strong academic–industry partnerships
Kobe is particularly notable as the birthplace of “hinotori”, Japan’s first domestically developed surgical robot, created by Medicaroid, a collaboration between Sysmex Corporation and Kawasaki Heavy Industries. Kansai’s innovation-driven environment accelerates robotic adoption across multiple hospitals.
Aichi: Advanced Manufacturing Meets Medical Robotics
Aichi Prefecture—anchored by Nagoya—leverages its world-leading industrial ecosystem to support medical technology. This region benefits from:
Strong engineering and manufacturing talent
Widespread adoption of robotic technologies in hospitals
Collaboration between healthcare and industrial giants
Several hospitals in Aichi have already installed the “hinotori” robot, providing a more affordable alternative to foreign systems.
Additional Regions: Expanding but Uneven Growth
Other prefectures—Kanagawa, Saitama, Hyogo, Chiba, Hokkaido, Fukuoka, and Shizuoka—show steady but unequal growth. Cost barriers and training gaps restrict adoption in rural zones, but government initiatives aim to gradually close this gap.
Market Segmentation
By Component
Surgical Systems
Accessories
Services
By Area of Surgery
Gynecological Surgery
Cardiovascular
Neurosurgery
Orthopedic Surgery
Laparoscopy
Urology
Other Surgeries
By Cities
Tokyo, Kansai, Aichi, Kanagawa, Saitama, Hyogo, Chiba, Hokkaido, Fukuoka, Shizuoka
Key Companies Covered
Each company includes an overview, key persons, recent developments, SWOT analysis, and revenue analysis:
Intuitive Surgical Inc.
Stryker Corporation
Johnson & Johnson
Renishaw PLC
Accuray Incorporated
Titan Medical Inc.
Medtronic PLC
Smith & Nephew PLC
Zimmer Biomet
These players are advancing robotics globally through innovation in surgical systems, training, imaging, precision tools, and automation.
Final Thoughts
Japan stands on the brink of a surgical revolution. With its rapidly aging society, accelerating technological capabilities, and significant government backing, the nation is fast becoming a global hub for next-generation surgical robots. From homegrown innovations like the hinotori system to widespread deployment of advanced robotic platforms in Tokyo, Kansai, and Aichi, Japan’s healthcare system is evolving toward precision, efficiency, and patient-centered outcomes.
Between 2025 and 2033, the market’s upward trajectory—reaching US$ 717.75 million by 2033—signals more than just economic growth. It reflects a future where minimally invasive, AI-assisted, robotics-powered surgeries become the norm, reshaping patient care for generations.
If current trends continue, Japan’s surgical robotics ecosystem will not only strengthen its domestic healthcare system but also export technologies and expertise worldwide—solidifying its role as a pioneer in the global medical robotics arena.

AloJapan.com