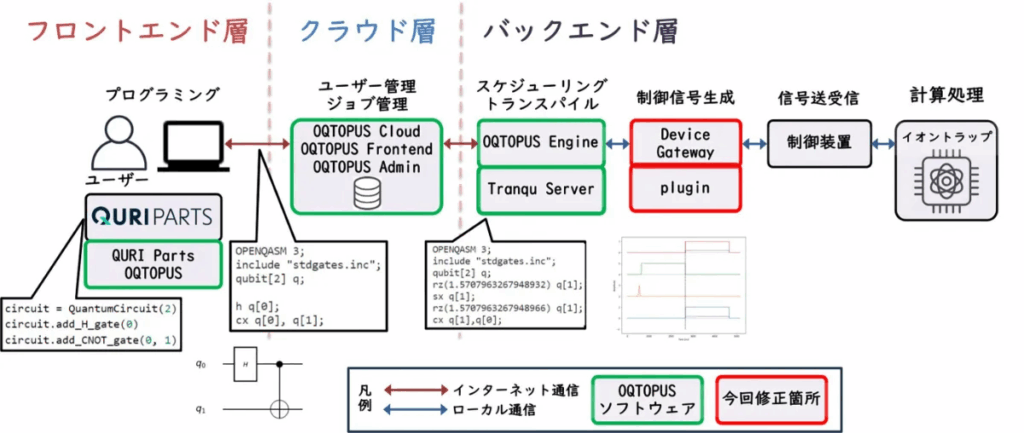
A research group at the Osaka University Center for Quantum Information and Quantum Biology (QIQB), led by Lecturer Koichiro Miyanishi and Professor Kenji Toyoda, has successfully developed and tested a system that enables the remote operation of an ion trap quantum computer via the cloud. This represents the first instance in Japan of an ion trap quantum computing environment that integrates all necessary technological elements—from the ¹⁷¹Yb⁺ linear Paul trap device to the control system and cloud software—to execute a single-qubit gate remotely.
To ensure stable, long-term remote use, the system incorporates essential automation technologies, including automatic ion loading, automatic laser position correction, and continuous status monitoring. This integrated control system allows the ion trap qubits to be maintained without researchers having to directly interact with the equipment, paving the way for a quantum computing platform capable of 24-hour operation. The cloud connection is realized using the open-source software platform OQTOPUS (Open Quantum Toolchain for Operators and Users), developed at Osaka University QIQB.
The research established the fundamental technology for stable remote operation, confirming qubit state preparation and readout with 94% fidelity and successful quantum state manipulation via Raman transitions. This system has significant potential for use in both research and education, providing continuous remote access to actual ion trap qubits. Future development efforts will focus on implementing two-qubit gates and operating multiple ion systems to accelerate the execution of quantum algorithms.
Read the full announcement from Osaka University QIQB here.
December 7, 2025



AloJapan.com